Sécheresse
Definition
Facts and figures
Further information
UN-SPIDER Regional Support Offices with hazard-specific expertise
Related content on the Knowledge Portal
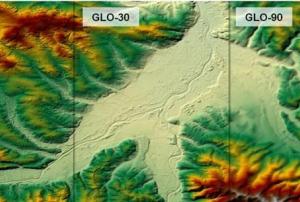
- The Copernicus DEM is a Digital Surface Model (DSM) which represents the surface of the Earth including buildings, infrastructure, and vegetation. The Copernicus DEM is provided in 3 different instances. Two worldwide coverages at 90m (GLO-90) and 30m (GLO-30) resolution are openly available to the public for download via the PANDA Catalogue and FTP. A further European coverage (EEA-10) is provided at 10m resolution, but data is restricted to eligible users who meet required access rights.Publishing institution:
- The Copernicus DEM is a Digital Surface Model (DSM) which represents the surface of the Earth including buildings, infrastructure, and vegetation. The Copernicus DEM is provided in 3 different instances. Two worldwide coverages at 90m (GLO-90) and 30m (GLO-30) resolution are openly available to the public for download via the PANDA Catalogue and FTP. A further European coverage (EEA-10) is provided at 10m resolution, but data is restricted to eligible users who meet required access rights.Publishing institution:
Southern Africa is exposed to hydrometeorological, geological, coastal and biological hazards. The region has been hard hit by droughts in recent years. Tropical cyclone Idai triggered massive floods in Mozambique, Malawi, and Zimbabwe in March 2019, and in 2020 several countries experience a severe locust outbreak. And unfortunately, COVID-19 continues to impact all countries in this region.
To continue efforts to promote the use of space technologies in disaster risk management, emergency response and recovery efforts, UN-SPIDER and the Centre for Remote Sensing of Land Surfaces of the University of Bonn (ZFL) joined forces to organize the UN-SPIDER / ZFL Regional Virtual Expert Meeting for Southern Africa "Space-based Solutions for Disaster Risk Management and Emergency Response" from 13 to 15 July 2021. This regional expert meeting contributed to the efforts conducted by UN-SPIDER on disaster risk reduction, preparedness, early warning…
read moreRegional Support Offices mentioned:19/07/2021África del Sur está expuesta a amenazas hidrometeorológicas, geológicas, costeras y biológicas. En los últimos años la región ha sufrido los impactos de sequías, inundaciones y plagas de langosta. La tormenta tropical Idai provocó inundaciones severas en Mozambique, Malawi y Zimbabue en marzo del año 2019 y en el año 2020 varios países tuvieron que afrontar la plaga de langosta. Desafortunadamente, COVID-19 sigue impactando a todos los países de esta región.
Para continuar promoviendo el uso de tecnologías espaciales en actividades relacionadas on la gestión para la reducción de riesgo de desastres, la preparación, la respuesta y la recuperación en caso de desastres, ONU-SPIDER y el Centro de Percepción Remota de Superficies Terrestres de la Universidad de Bonn (ZFL por sus siglas en inglés) unieron esfuerzos para organizar la Reunión Regional Virtual de Expertos para África del Sur: "Soluciones Espaciales para Gestión de Riesgo y Respuesta en caso…
read moreRegional Support Offices mentioned:19/07/2021Southern Africa is exposed to hydrometeorological, geological, coastal and biological hazards. The region has been hard hit by droughts in recent years. Tropical cyclone Idai triggered massive floods in Mozambique, Malawi, and Zimbabwe in March 2019, and in 2020 several countries experience a severe locust outbreak. And unfortunately, COVID-19 continues to impact all countries in this region.
To continue efforts to promote the use of space technologies in disaster risk management, emergency response and recovery efforts, UN-SPIDER and the Centre for Remote Sensing of Land Surfaces of the University of Bonn (ZFL) joined forces to organize the UN-SPIDER / ZFL Regional Virtual Expert Meeting for Southern Africa "Space-based Solutions for Disaster Risk Management and Emergency Response" from 13 to 15 July 2021. This regional expert meeting contributed to the efforts conducted by UN-SPIDER on disaster risk reduction, preparedness, early warning…
read moreRegional Support Offices mentioned:19/07/2021Droughts have extensive and profound repercussions on populations, livelihoods, ecosystems, and economies. The most vulnerable people are unduly affected by their financial consequences. Although droughts affect millions, lead to food shortages, poverty, and inequality, their immense and widespread effects are often underreported.
Climate change is aggravating the intensity, duration, and prevalence of droughts globally through rising temperatures and disturbances of rainfall patterns. Within the next 80 years, climate change will be the primary cause of the increased drought exposure of 129 countries (Smirnov et al., 2016). As global temperatures rise due to climate change, pressing action is needed to manage the risks related to droughts, and to diminish their destructive impact on human lives, livelihoods, and ecosystems.
On 17 June 2021, the United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD) celebrated the …
read more18/06/2021Introduction
Space-based applications related to Earth Observation and geospatial data play an important role in supporting disaster risk reduction, response, and recovery efforts through providing accurate and timely information for decision-makers. Monitoring floods, drought conditions and water resource environments using satellite remote sensing (RS) technologies have become more essential recently in particular for developing countries.
This workshop will address the use of space technologies (remote sensing, telecommunication and global navigation satellite systems) for various applications in natural disaster managements that can provide sustainable social and economic benefits. Current and planned projects/research that use space-based technologies for both practical applications and scientific explorations will be presented. Cooperative efforts and international partnerships for capacity-building, training and research will be discussed.…
read moreSpace-based applications related to Earth Observation and geospatial data play an important role in supporting disaster risk reduction, response and recovery efforts through providing accurate and timely information for decision-makers. Monitoring floods, drought conditions and water resource environments using satellite remote sensing (RS) technologies have become more essential recently, in particular for developing countries.
The workshop will be held in Tehran, Iran, from 9 to 11 August 2021, in a virtual format, and will be hosted by the Iranian Space Agency (ISA). The workshop will explore how current space technologies help identify and monitor the effects of a changing climate – including the onset of drought, flash floods, and general water resources conditions as a result of global climate change, in particular on an international and regional scale. The discussions at the workshop will also be linked to the 2030 Agenda for…
read moreRegional Support Offices mentioned:14/06/2021The United Nations Platform for Space-based Information for Disaster Management and Emergency Response (UN-SPIDER) and the Office of the State Ministry for Disaster Management and Humanitarian Affairs of the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan (ANDMA) carried out a virtual thematic meeting on ‘Assessing Drought and Water Resources Conservation Using Earth Observation’, in collaboration with Delta State University and the International Water Management Institute (IWMI). All key stakeholders involved in disaster risk reduction, especially dealing with drought, attended the meeting which was chaired by His Excellency Deputy Minister Mohammad Qasim Haidari. This meeting, held on 26 May 2021, is part of the UN-SPIDER Technical Advisory Support to Afghanistan. It was attended by 48…
read moreRegional Support Offices mentioned:09/06/2021