Tropical Storm Muifa appears huge on NASA infrared imagery
The width of an image from the AIRS instrument that flies on NASA's Aqua satellite is about 1700 km (1056 miles), and the clouds and thunderstorms associate with Tropical Storm Muifa take up that entire distance in the latest imagery. Tropical Storm Muifa is spinning through the western North Pacific Ocean Friday and has grown in size. When NASA's Aqua satellite passed over the storm on July 29, 2011 at 04:17 UTC (12:17 a.m. EDT) it measured the temperatures in the cloud tops. Those cloud top temperatures especially in the east and western sides of the tropical storm were colder than -62 Fahrenheit/-52 Celsius, indicating strong storms with heavy rainfall. Fortunately, much of that heavy rainfall was over open ocean.
For the full article: www.spacedaily.com/reports/Tropical_Storm_Muifa_appears_huge_on_NASA_infrared_imagery_999.html
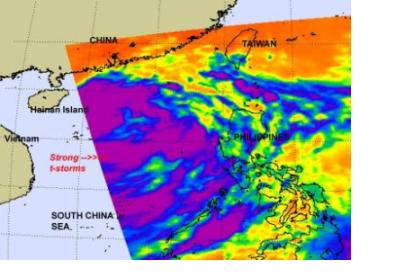
NASA eyes Tropical Storm Nock-Ten's heavy rains for Hainan Island and Vietnam
Infrared satellite imagery from NASA's Aqua satellite shows bands of strong thunderstorms wrapping around the center of Tropical Storm Nock-Ten as it makes its way through the South China Sea and two landfalls on Hainan Island and in Vietnam. Bands of strong thunderstorms that make up tropical storm Nock-ten were visible in an infrared image captured on July 28 by the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument that flies on NASA's Aqua satellite. The colder the cloud tops, the higher the thunderstorms and the stronger they are, and cloud top temperatures over a large area of Nock-ten were colder than -63 Fahrenheit (-52 Celsius) and the cloud tops likely extended into the tropopause. High, strong thunderstorms like those also can generate heavy rainfall, up to 2 inches (50 mm) per hour. Those in Nock-ten's path can expect heavy rainfall, local flooding, gusty winds and rough surf along coastal areas.
For the full article: http://www.eurekalert.org/pub_releases/2011-07/nsfc-net072811.php