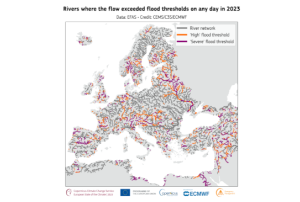
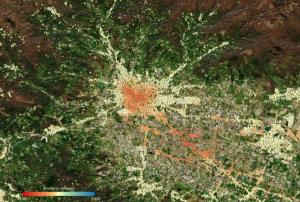
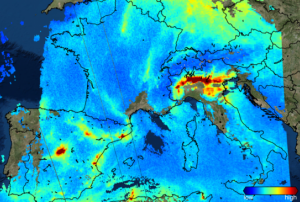
On 15th October, the European Space Agency (ESA) officially kicked off their new project, Ciseres, at the International Astronautical Congress (IAC) in Milan. Ciseres is a small satellite mission integrating AI directly into the process of identifying relevant information in satellite imagery. Users are provided with rapid “actionable” information within just a few minutes.
“AI-powered Satellite systems will redefine how we respond to disasters” (CEO of Deimos).
The Ciseres project is an initiative by ESA aiming at enhancing disaster response through the use of AI-powered satellites. As part of ESA's Civil Security from Space (CSS) programme, Ciseres is designed to significantly improve the speed and efficiency of crisis response by integrating AI directly into satellite operations. The project is a collaboration between ESA and several European companies, including Deimos, Skylabs, and GINA, each bringing their expertise to enhance the satellite's capabilities…
more