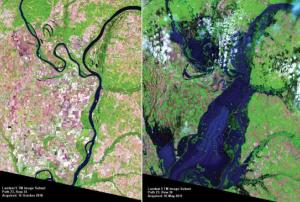
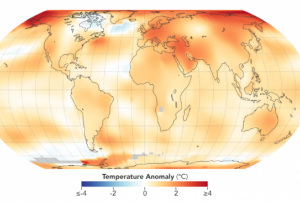
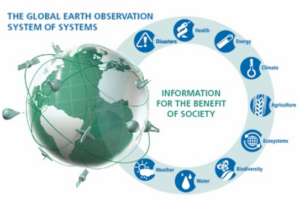
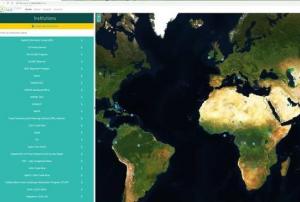
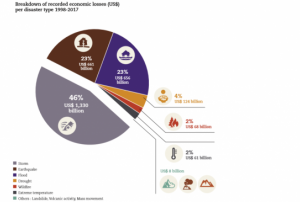
Representatives from the network of UN-SPIDER Regional Support Offices (RSO) convene in Vienna for the 9th Annual RSO Coordination Meeting from 18 to 19 June. Held at the United Nations Offices in Vienna, the meeting provides the 23 RSOs the opportunity to propose concrete ways in which they, respectively, could further collaborate with UN-SPIDER and also with other RSOs. The event is a forum for discussion of innovative approaches to disaster management using space-based technologies.
At the meeting, RSO representatives discussed lessons learned from their respective regional capacity-building and knowledge and awareness-raising activities, and their experiences working with the International Charter “Space and Major Disasters”. Additional discussions included the development and…
more