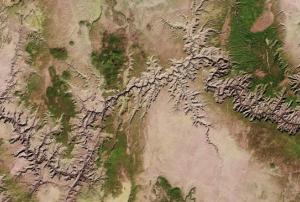
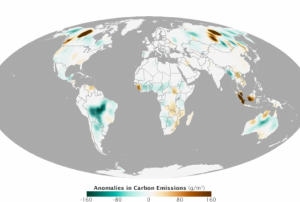
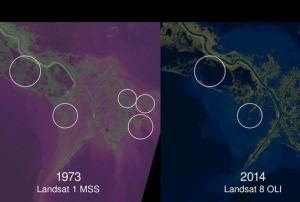
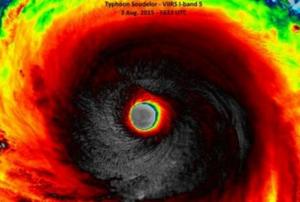
An Open-ended Intergovernmental Expert Working Group on Indicators and Terminology was established by the UN General Assembly in June 2015, as a way to steer efforts regarding indicators to assess advances in the context of the seven targets established in the Sendai framework for Disaster Risk Reduction 2015-2030. The experts in this OEIWG are nominated by Member States (countries). By June 2016, 255 experts form 107 Member States have been nominated to participate in the OEIWG.
UNDRR organized the third meeting of the OEIWG in September 2015 to examine and discuss the indicators to monitor the 7 Global Targets established on the Sendai Framework. The whole document is available …
more