The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) has released the first photographs collected by its GOES-19 satellite, which provide a nearly constant view of the Western Hemisphere. GOES-19, the most recent addition to NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellites (GOES) network, was launched on 25 June 2024. The Advanced Baseline Imager (ABI) on GOES-19 takes data throughout 16 channels of the electromagnetic spectrum, including the visible, near-infrared, and infrared bands.
The preliminary images, taken on August 30, 2024, demonstrate the capacity of GOES 19 to track meteorological, climatic, and environmental hazards in near real time.
The satellite spotted a variety of occurrences, including wildfires, storms, and severe weather events like Hurricane Francine, which impacted Louisiana recently. NOAA intends to transfer GOES-19 to full operations by April 2025, replacing GOES-16 as the operational GOES-East, after which the satellite will undertake post-launch testing and calibration.
Like its predecessors, GOES 19 will contribute to monitor hydro meteorological hazards in near time, providing key data for the routine operation of early warning systems launched to address these types of natural hazards.
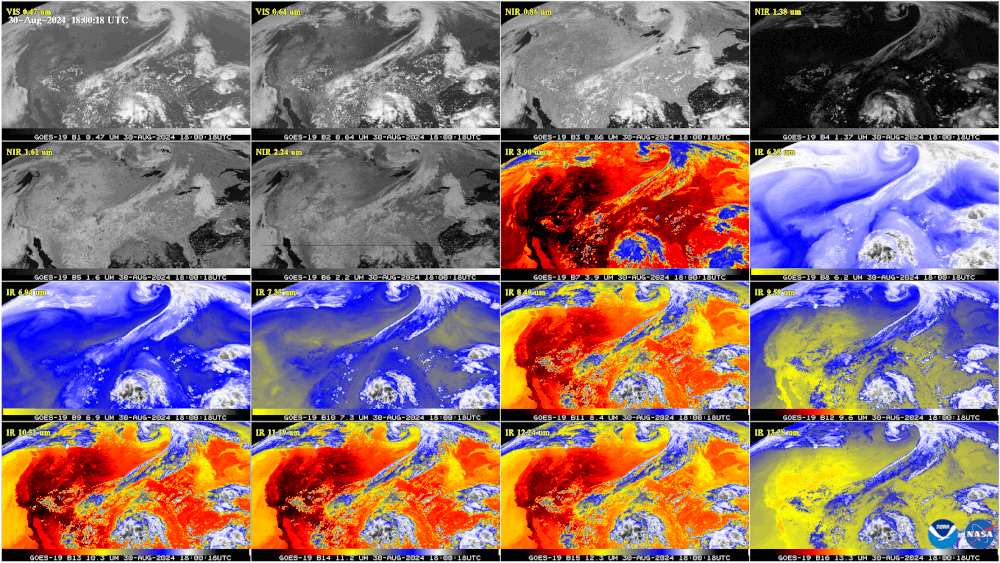
This GOES-19 image shows the contiguous United States observed by each of the ABI’s 16 channels on Aug. 30, 2024. This 16-panel image shows the ABI’s two visible, four near-infrared and 10 infrared channels. The visible and near-IR bands are gray-colored, while the infrared bands have the warmer brightness temperatures mapped to warmer colors. The different appearance of each band is due to how each band reflects or absorbs radiation. Each spectral band was scanned at approximately the same time, starting at 18:00 UTC.
Martin article image: GOES-19 full disk GeoColor image from Aug. 30, 2024. This type of imagery combines data from multiple ABI channels to approximate what the human eye would see from space.

