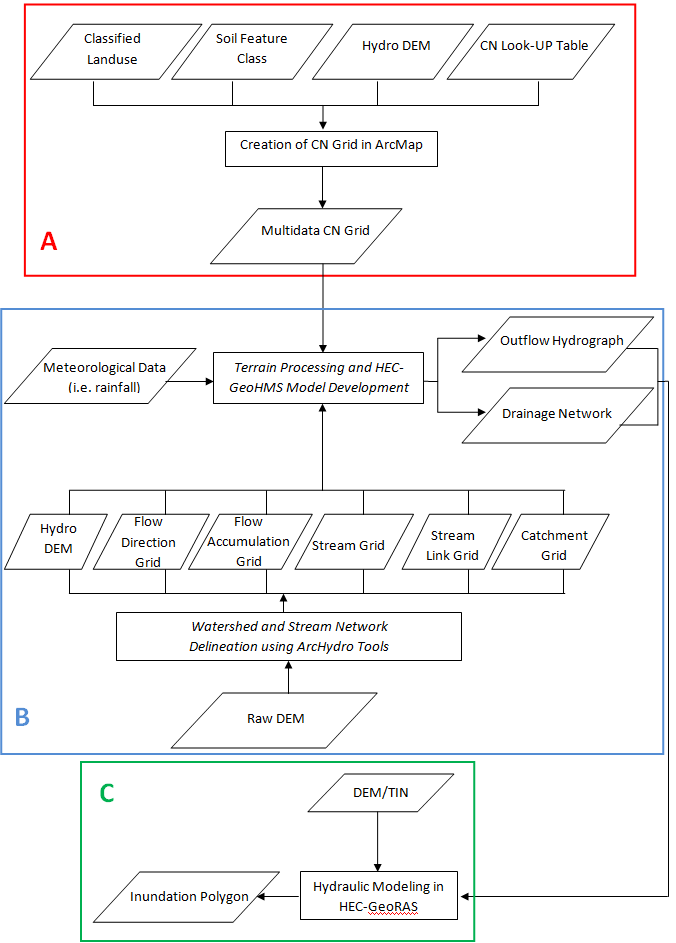
- Data requirements: (1) Digital elevation model (DEM) for the study area; (2) Soil data (e.g. SSURGO); (3) Land cover data (e.g. 2006 Land cover grid from USGS); (4) hydrography data (mainly stream network)
- Image preprocessing can be carried out using any commercial or free remote sensing software;
- For visualization and creation of maps, we will use ArcGIS version 10 (not free);
- For hydrological modelling we will use ArcHydroTool, Hec-GEoRAS and Hec-GeoHMS for ArcGIS 10 (free). (cf. right column to access related software)
- Skills requirements: intermediate to advanced knowledge of image processing, GIS and hydraulic modelling.
Strenghts:
- Efficient tool to predict potential flood hazards for vulnerable areas;
- Useful for the development of local prevention strategies;
- Useful for the facilitation of emergency response and efforts coordination during extreme events;
- Improvement of information accessibility;
- Storage of information that can be useful in future situations.
Limitations:
- Highly accurate DEM data are required;
- Availablility of observational data for model assessment;
- Calibration of the hydrological model requires knowledge of the study area and experience;
- High sensitivity to boundary conditions.
Larose M. et al., 2007. American Society of Agronomy, Crop Science Society of America, Soil Science Soiety. ASA, CSSA, SSSA. Online available at https://www.certifiedcropadviser.org/publications/jeq/abstracts/36/2/521?access=0&view=article
Merwade V., 2012. Creating SCS Curve Number Grid using HEC-GeoHMS. School of Civil Engineering, Purdue University. Online available at http://web.ics.purdue.edu/~vmerwade/education/cngrid.pdf
Merwade V., 2012. Terrain Processing and HMS-Model Development using GeoHMS. School of Civil Engineering, Purdue University. Online available at http://web.ics.purdue.edu/~vmerwade/education/geohms.pdf
Merwade V., 2012. Watershed and Stream Network Delineation using ArcHydro Tools. School of Civil Engineering, Purdue University. Online available at http://web.ics.purdue.edu/~vmerwade/education/terrain_processing.pdf
US Army Corps of Engineers - Hydrologic Engineering Center, 2009. HEC-GeoRAS, GIS Tools for Support of HEC-RAS using ArcGIS. Online available at http://www.hec.usace.army.mil/software/hec-georas/documentation/HEC-GeoRAS4_UsersManual.pdf
| Attachment | Taille |
|---|---|
| FLOOD HAZARD MAPPING_Mazimwe.pdf | 3.3 MB |
