
Space technologies and geospatial data can support governments in improving situational awareness and responding to the COVID-19 outbreak. Several institutions have published information products, such as web maps of confirmed infections and deaths, that are making use of the advantages of GIS. Others have used space technologies to track pollution levels across the world, highlighting a drop due to the restrictions imposed as a result of the pandemic. Yet others are using a combination of global navigation satellite systems technologies to map the position of critical infrastructure in geographical areas where there are reported cases.
The United Nations Office for Outer Space Affairs, through its UN-SPIDER programme, has created this COVID-19 emergency response overview page to facilitate the discovery of examples of contributions of space technologies to addressing COVID-19 that are being published by government agencies, international and regional organizations, academia, civil society and the private sector. To find out more about the efforts of UNOOSA in advancing the use of space-based solutions for global health, please visit this web page.
To support users in finding relevant content, the list below can be filtered by keywords as well as format of the resource. The list does not seek to be exhaustive, nor to recommend particular sources, but to provide a selection of examples of how space technologies and the space community support response efforts to COVID-19.
UNOOSA will host a webinar on Space4Health on 14 May at 10am and 4pm Vienna, Austria time (UTC+2).
If you are using space technologies for responding to the COVID-19 pandemic and would like your work to be included on this page, please use this form to submit details.
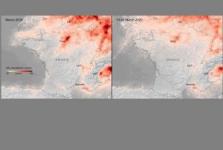
Scientists from the Royal Netherlands Meteorological Institute (KNMI) have been using data from Copernicus Sentinel-5P satellite, launched in 2017, to monitor both weather and pollution over Europe. The new images clearly illustrate a strong reduction of nitrogen dioxide concentrations over major cities across Europe. The analysis… Read more
Tag: (Indirect) impact of the virus
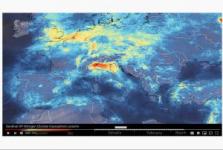
Data from the Copernicus Sentinel-5P satellite show the decline of air pollution, specifically nitrogen dioxide concentrations, over Italy. This reduction is particularly visible in northern Italy which coincides with its nationwide lockdown to prevent the spread of the coronavirus.
The animation shows the fluctuation of nitrogen dioxide… Read more
Tag: (Indirect) impact of the virus

Google has published Community Mobility Reports that display the change in visits to places such as grocery stores and parks. The reports are created with aggregated, anonymized sets of data from users who have turned on… Read more
Tag: (Indirect) impact of the virus

Published by the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control, the dataset contains the latest available public data on COVID-19 including a daily situation update, the epidemiological curve and the global geographical distribution (EU/EEA and the UK, worldwide).
Since the beginning of the coronavirus pandemic, ECDC’s… Read more
Tag: Situational data

ESA in coordination with the European Commission is launching a special edition of the Custom Script Contest, focused on the support of space assets during the COVID-19 crisis, managed by Euro Data Cube group. The contest calls for remote sensing experts, machine… Read more
Tag: (Indirect) impact of the virus

UN News reports that United Nations weather experts warned on Wednesday, 1 April, that the coronavirus pandemic risks disrupting key forecasting services, including early warning alerts around the world.
Both the quantity and quality of weather observations and forecasts, as well as atmospheric and… Read more
Tag: (Indirect) impact of the virus
According to the World Meteorological Organization (WMO), the COVID-19 pandemic is negatively affecting the quantity and quality of weather observations and forecasts, as well as atmospheric and climate monitoring. Meteorological measurements taken from aircraft have indeed dropped by an average 75-80 percent compared to normal. As the Atlantic… Read more
Tag: (Indirect) impact of the virus
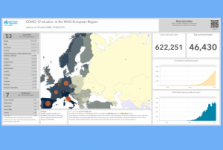
Tag: Situational data, UN activities
The COVID-19 pandemic is affecting most aspects of everyday life, including air travelling. Commercial flights usually collects measurements of temperature, wind speed and wind direction in the atmosphere, and provide useful and accurate information for weather forecasts. However, measurements from aircraft have dropped by 90% in the last few… Read more
, Web page
Tag: (Indirect) impact of the virus

In light of the COVID-19 outbreak, the Government of Luxembourg will make access to the SATMED platform available free of charge for healthcare professionals’ community of selected health organisations to fight the pandemic.
SATMED is a multi-level software-as-a-service eHealth platform owned by the Government of… Read more
Tag: Emergency mapping, Tele-health
The Digital Earth Africa has released high-resolution images captured by Sentinel-2 satellites to enable countries to monitor changes that relate to people and the environment due to the impacts of COVID-19 and other critical challenges. The images, which are available in a format that makes them accessible and suitable for general use, offer… Read more
Tag: Situational data, Risk assessments, (Indirect) impact of the virus
The Canadian company GHGSat and the RON Netherlands Institute for Space Research have worked together to investigate hotspots of methane emissions during COVID-19. Using measurements from Sentinel-5P and GHGSat satellites, they were able to quantify and attribute the… Read more
Tag: Situational data, (Indirect) impact of the virus

