Tsunami
Definition
Facts and figures
Further information
UN-SPIDER Regional Support Offices with hazard-specific expertise
Related content on the Knowledge Portal
In 2015 the United Nations declared that each year 5 November would be observed as World Tsunami Awareness Day – a reminder that when a tsunami strikes, everyone must be ready to get to high ground.
Like all disasters, tsunamis have an unequal and unique impact on the affected population. Poverty levels, exposure, discrimination and other vulnerabilities all play a key role in determining who is likely to be affected and how. For example, following the Indian Ocean tsunami of 2004 that affected 12 countries, it was found that poor households were more likely to see their “flimsy houses” wash away, while the brick houses of richer households proved sturdier.
Satellites equipped with specialized sensors can detect and monitor various indicators, such as sea surface temperatures, ocean currents, and underwater seismic activities. By analyzing these data, scientists can identify potential tsunami-triggering events, like underwater earthquakes or volcanic eruptions.…
read more06/11/2023World Tsunami Awareness Day
In 2015 the United Nations declared that each year 5 November would be observed as World Tsunami Awareness Day – a reminder that when a tsunami strikes, everyone must be ready to get to high ground.
Tsunamis can be deadly, but they needn’t be. Early warning and early action are effective tools to protect people, saving lives, and preventing the hazard from becoming a disaster. To be effective, tsunami early-warning systems must cover every at-risk person, they must be multi-hazard, and communities must be prepared so they can act quickly.
Find more information on the World Tsunami Awareness Day here.
05/11/2022Implementing science to save lives: A Decade of the Copernicus Emergency Management Service
The Copernicus Emergency Management Service (CEMS) celebrates a decade of operation as a world leader in emergency mapping, early warning tools and open-access disaster information.
For the past ten years, CEMS has provided a global service as a fully operation emergency mapping service at no cost to users and with open access data.
Some highlights on the contribution of CEMS in global disaster risk management activities:
- 576 Rapid Mapping Activations with 5,500+ maps delivered
- Designed and implemented the world’s first Global Flood Monitoring tool
- Ten years of wildfire forecasts up to ten days into the future
- Average of 200+ flood and 500+ flash flood notifications to Member States and authorised users each year
- Offers a current and historical database of 7,000+ drought episodes since 1950
…
read more22/06/2022Matthew Blackett, Coventry University
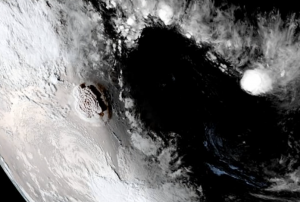
The scale of a recent volcano eruption took the people of Tonga by surprise. Scientists monitoring the submarine volcano, Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha'apai, were likewise caught off-guard, failing to foresee an explosion which would unleash a Pacific-wide tsunami.
The scale of the eruption was hailed as a “once in a millenium” event by one scientist. It hurled gasses and ash over 39km into the atmosphere – comparable to that ejected from Mount Pinatubo in 1991 – and generated a…
read more28/01/2022On the 13th and 15th of January 2022 the underwater volcano on Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’pai, located in the South Pacific Kingdom of Tonga erupted. The eruption on the 15th of January 2022 was seven times more powerful than the first eruption of the volcano, which took place on the 20th of December 2021. Additionally, it led to a tidal gauge, resulting in a tsunami wave that impacted countries in the Pacific Ocean, from the Kingdom of Tonga, Australia and New Zealand, Japan, up to Peru, among others, on the other side of the Pacific.
The volcanic eruption was captured by the GOES-West Earth-observing satellite operated by the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), as well as by the Himawari-8 satellite, operated by the Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA), resulting in spectacular images, revealing the large extent of this event.
This is an example of the capacity of geostationary satellites and the benefit of meteorological satellites tracking large…
read more18/01/2021The United Nations Office for Outer Space Affairs (UNOOSA) and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration of the United States Government (NASA) signed a landmark Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) on 17 December 2020 pledging cooperation in areas of science and technology to support the peaceful uses of outer space.
The MoU brings together NASA's wealth of open-source spacecraft data, tools, and expertise and UNOOSA's unique position as the only UN entity dedicated to outer space affairs, to expand global opportunities to leverage the benefits of space. The partners will design capacity-building programmes, particularly for institutions in countries that do not yet have or that are developing space capabilities, to help them access space.
Together, UNOOSA and NASA will develop ways to leverage the Artemis programme as part of UNOOSA's Access to Space 4 All Initiative, which offers opportunities for international researchers and institutions, especially in…
read more11/01/2021The European Commission plans to rapidly expand its environmental monitoring programme Copernicus. For this purpose, the European Space Agency (ESA) recently pledged 2.55 billion Euros towards contracts to advance the production of six new Copernicus satellite missions. The final of the six contracts was signed last Thursday between ESA and Thales Alenia Space for a mission that will provide new and important information to climate research and disaster management.
The high-priority Copernicus Radar Observation System for Europe in L-band (ROSE-L) mission is planned to launch in 2028 for a period of 7.5 years. The ROSE-L mission will orbit Earth every few days at an altitude of 690km and will carry a L-Band synthetic aperture radar (SAR). With a wavelength of approximately 23cm, an…
read more18/12/2020The Disasters programme unit at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) recently joined a newly launched online platform aimed at placing anticipatory action on the humanitarian agenda. NASA’s involvement in the Anticipation Hub and the subsequent incorporation of Earth observation (EO) tools, serves to improve the capabilities of anticipatory action globally and demonstrates the potential of utilizing satellite-driven data for anticipatory action in disaster management.
Anticipatory action in the humanitarian context describes disaster mitigation activities based on in-depth forecast information and risk analysis. This approach has gained traction amongst the humanitarian community in recent years as it is viewed as a more efficient and affordable alternative…
read more02/02/2021A new report outlines the impact of Global Human Settlement Layer (GHSL) data on various policy areas. The 2020 edition of the “Atlas of the Human Planet”, recently published and launched virtually by the Joint Research Centre (JRC) of the European Commission as a deliverable to the Group on Earth Observations (GEO) Human Planet Initiative, explores the impact of GHSL data on various policy areas, including disaster risk management.
GHSL data refers to “global spatial information, evidence-based analytics and knowledge describing the human presence on the planet”. This data relies on spatial information from Landsat 8, Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2. It is mainly cost-free and…
read more18/02/2021The use of multi-risk information systems is crucial in confronting the increasing risks posed by natural hazards. In some cases, risk is increasing due to inadequate land-use norms or regulations that allow for the construction of infrastructure in areas exposed to such natural hazards. In other cases, vulnerability increases due to lack of awareness or extreme poverty. The need to address risks from the point of view of multiple hazards is necessary to contribute to sustainable development and has been incorporated as an essential element of the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction 2015-2030. For this purpose, the RIESGOS 2.0 project was launched in March 2021. Under the coordination of the German Aerospace Center (DLR), the project builds on the accomplishments of its predecessor - RIESGOS - as a multi-risk information system that models and simulates natural…
read more17/03/2021