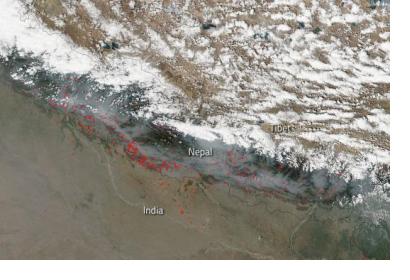
In Nepal, SERVIR-Hindu Kush Himalaya at the International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD), a UN-SPIDER Regional Support Office (RSO), has been working in close collaboration with the Department of Forests of Nepal to develop a satellite-based forest fire detection and monitoring system. The system uses Earth observation data with large-area repetitive coverage to facilitate near real-time forest fire detection, monitoring, and area assessments.
Forest fires have a detrimental ecological and even economic effect upon Nepal, especially during Nepal’s long and dry summers. They also pose a serious threat to properties and lives in the country, with the 2016 forest fires reportedly killing 15 people and burning an area of 13,000 square kilometres.
In order to tackle the issue of forest fires, ICIMOD and the Department of Forests of Nepal established a disaster management system that uses satellite data to provide those communities affected by or living in at risk area with critical real time information on forest fires.
The forest fire detection and monitoring system uses satellite data from the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) aboard NASA's Terra and Aqua satellites, whose data can be used to track changes in landscape over time. Data collected as well as images taken by these satellites can be accessed for free by the public on NASA’s Wordview site.
If a forest fire is detected in the data acquired by the satellites, the system alerts subscribers in the affected area via text message within 20 minutes of the initial detection, allowing District Forest Officers the opportunity to prepare and local communities the chance to evacuate. A web mapping application uses the satellite data and information to visualize the locations of forest fires and users can browse fire locations on any user-specified time period as well as being able to download maps of forest fire incidences on any given day.
The system is key in supplying many actors, such as local police, army, and local communities, with relevant and timely information and this information is especially important in mobilizing immediate response towards the fires.
ICIMOD has also worked on upgrading the system by integrating data from the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS), one of the key instruments onboard the Suomi National Polar-Orbiting Partnership (Suomi NPP) spacecraft, to compliment the MODIS data. The combination of VIIRS and MODIS data allows for better mapping of fires and also improved the spatial resolution of fires in precise areas.
The data from these space-based instruments is also used in a mobile application called Nepal Forest Fire Detection and Alert. The application supports the disaster management process by supporting citizens on the ground reporting of forest fires. Better information, both spatial and ground information, leads to better planning and resource allocation during the disaster management process.
The forest fire management system has been successfully implemented and integrated into disaster management processes in Nepal, and after its successful implementation, the system will be expanded to cover Bhutan in the near future.