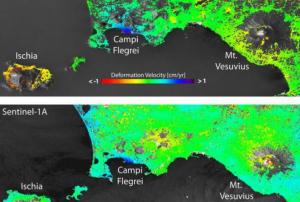
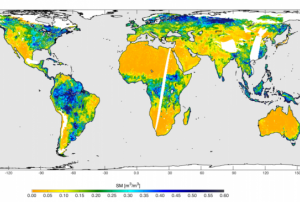
The US National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (NGA) and DigitalGlobe have jointly released Hootenanny, a new open source project to enhance the way crowdsourced mapping influence geospatial big data analytics.
Through GitHub, a web-based Git repository hosting service, Hootenanny provides a scalable processing engine and interactive editing interface to help users rapidly conflate, or reconcile, map features generated from satellite imagery, unmanned aerial vehicles and mobile devices, as NGA explained.
“The commercialization of GEOINT [GEOspatial INTelligence] is leading to exponential growth of publicly available geospatial information. Hootenanny as an open source project will enable new levels of data sharing across the community that will increase our nation’s ability to quickly respond to emerging…
more