Inondation
Definition
Facts and figures
Further information
UN-SPIDER Regional Support Offices with hazard-specific expertise
Related content on the Knowledge Portal
- SAR-based flood mapping is a standard and reliable method for determining the extent of major floods. SAR can penetrate cloud-cover, operate in any weather conditions and provide timely and crucial information about one of the most frequent and devastating natural disasters: flooding. Too often limited technical know-how separates the disaster community from the information they need; this Recommended Practice provides a near real-time, cloud-based and easy-to-use method for flood extent mapping, designed to overcome technical limitations. Without the need for downloading large and complex…
In order for South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) Member States to be able to incorporate the routine use of space technology-based solutions, there is a need to increase awareness, build national capacity and develop solutions that are customized to their needs. The regional workshop and capacity-building programme on the "Role of Earth Observation in Multi-Hazard Disaster Risk Assessment and Monitoring Targets of the Sendai Framework" is the second regional event in South Asia under the umbrella of the SAARC Disaster Management Center and the United Nations Office for Outer Space Affairs (UNOOSA), through its UN-SPIDER programme. The event took place in collaboration with the International Water Management Institute (IWMI), Sri Lanka, the Space Applications Centre of the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and the Centre for Space Science and Technology Education in Asia Pacific (CSSTEAP). It was built on the outcome of the first regional workshop and…
read moreRegional Support Offices mentioned:12/12/2019- OneAtlas is a collaborative environment to easily access very high resolution imagery, perform large-scale image processing, extract industry specific insights and benefit from Airbus assets to develop solutions. The services include infrastructure change detection, vehicle detection & counting and will soon cover aircraft detection and land use change detection as well . Airbus provides the services through a buy-what-you-need option. It is possible to test the functionalities with a 30-days Free Trial.Publishing institution:
- The Digital Earth Africa (DE Africa) Map is a website for map-based access to spatial information. It’s is still being developed by Data61 CSIRO in collaboration with Geoscience Australia. DE Africa is leveraging international Earth Observation (EO) data and science to produce new information and services that benefit African countries. Through translating data into ready-to-use insights, more informed decisions about soil and coastal erosion, agriculture, deforestation, desertification, water quality and changes to human settlements can be made. The data is organized in data-cubes and will be fully available by 2020.Publishing institution:
- Flood hazard assessments are critical to identifying areas at risk and taking relevant preparation and mitigation measures to address the hazard. Using the HEC-RAS 2D model for preparing flood hazard maps, this Recommended Practice explains how to identify flood-prone areas and exposed infrastructure. Through its focus on the prevention and mitigation stages of the disaster management cycle, it complements the Recommended Practice on Flood Mapping and Damage Assessment with Sentinel-2, also developed by SUPARCO.Regional Support Offices mentioned:
The training date is in the past. However, videos and resources of the training can be accessed here.
This training builds on the skills taught in previous ARSET SAR trainings in terms of the use of Google Earth Engine for flood mapping with radar data. This training presents two new topics; the use of InSAR for characterizing landslides and the generation of a digital elevation model (DEM).
Learning Objectives:
By the end of this training, attendees will be able to:
- Create a flood map using Google Earth Engine
- Generate a map characterizing areas where landslides have occurred
- Generate a digital elevation model (DEM)
read moreCourse Format:- This webinar series will consist of three, two-hour parts…
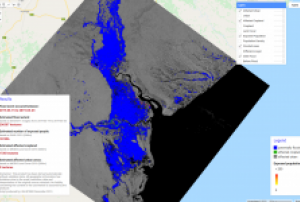
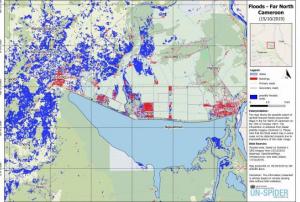
The 2019 rainy season in the Far North region of Cameroon has caused the Logone river to overflow and flood the Zina (Logone-et-Chari department), Maga and Kai-Kai districts (Mayo Dany) in the country's Far North region. The United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs reports that at least 60 out of 110 villages in the Zina district - 19,359 people - are affected, while 15 villages with a total of 16,215 people are affected in the Kai-Kai district.
UN-SPIDER has requested the activation of the International Charter Space and Major Disasters for the floods on behalf of the Department of Civil Protection (DPC) of Cameroon. SERTIT is acting as the project manager for this activation. An…
read more19/10/2019The 2019 rainy season in the Far North region of Cameroon has caused the Logone river to overflow and flood Zina district in the Logone-et-Chari department. According to media reports, the floods have left at least 100.000 people on both sides of border between Cameroon and Chad. While the rainy season in Cameroon typically takes place between May and September, this year's heavy rains have continued throughout October.
UN-SPIDER has requested the activation of the International Charter Space and Major Disasters for the floods in Cameroon on behalf of the Department of Civil Protection (DPC). SERTIT is acting as the project manager for this activation.
In July 2019, UN-SPIDER conducted an Institutional Strengthening Mission to Cameroon and ran a workshop focussing on making…
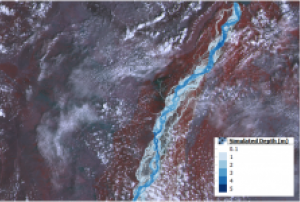
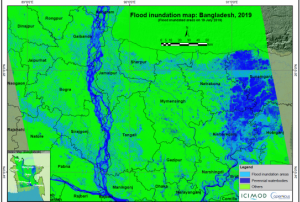
read moreIn July 2019, Bangladesh, India and Nepal experienced floods and landslides during the South Asian monsoon season. On the night of the 17 July, the Jamuna river in Bangladesh broke through the embankment, inundating over 40 villages and displacing more than 200,000 people. Experts of the International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD), a UN-SPIDER Regional Support Office, prepared flood inundation maps after the floods struck Bangladesh. By making use of free satellite data from the Sentinel-1 satellite of the Copernicus programme, ICIMOD experts were able to create maps that give a synoptic overview of the extent of inundation caused by the floods.
Flood inundation maps aid disaster management agencies in prioritizing relief and rescue missions in flood affected areas. These endeavors illustrate the usefulness of satellite data in emergency response: Maps play a crucial role in planning effective and efficient emergency response missions…
read moreRegional Support Offices mentioned:25/09/2019- Floods and landslides are the first and fourth most frequent disasters around the world (Petley, 2012). There are several examples of downstream flooding caused by massive mudslides where rapid mapping is an indispensable tool for supporting disaster management activities by civil protection authorities.Since July 2014, the Copernicus programme of the European Union has been providing free-of-charge access to Sentinel-1 radar data coveirng the entire world. This allows for the exploration of new applications to strengthen hazard monitoring and disaster mitigation activities.This UN-SPIDER…