The purpose of this recommended practice is to monitor the impacts of meteorological drought on natural vegetation (rainfed, rangeland & forest). Availability, simplicity, free of charge data, good research literature and citation, minimum requirements of inputs are the main criterion, which has been considered to define the methodology.
The test site used for the step-by-step instructions for ENVI includes the following five provinces in Iran: Alborz, Tehran, Semnan, Qom, Isfahan (See "In Detail for maps of the test site.).
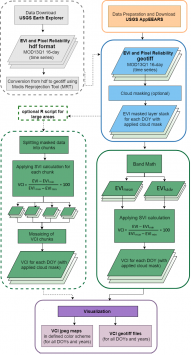
The original R script as well as the R script including a cloud mask have focused on Guatemala, while the R script for large areas has calculated the Vegetation Condition Index (VCI) for Peru.
The Python code has been tested for Ghana.
The total area of the test site in Iran amounts around 250,000 km2. The elevation within the test site ranges from 270m to 4,390m. The vegetation growth period is from May to June. The average annual rainfall amounts to 240mm. The predominant land cover is bare land and rangeland with mainly low vegetation density. Land cover of the test site also includes irrigated agriculture, rainfed agriculture, saline land, and seasonal lakes. Land cover classes with smaller occurrence include forest, orchard, and wetlands (see "In Detail" for maps of the test site).
Central American countries have experienced more frequent and intense droughts in the last two decades. These droughts have manifested themselves in arid areas of this regions, and have a greater impact on subsistence farmers. The worse effects and impacts have taken place when an international stressor (extreme reduction in the price of an agricultural export crop such as coffee in the world markets; or the substantial increase in the price of oil in the international markets) coincides with a severe drought. Governments have identified a certain geographic area in this region as the one most prone to the effects of droughts which is called the "Dry Corridor" of Central America.
The methodology as such can be applied globally. However, the choice of the months of the MODIS data will vary depending on the timing of the vegetation period.