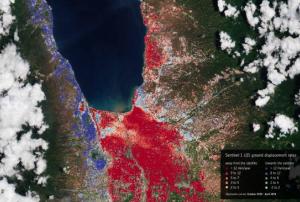
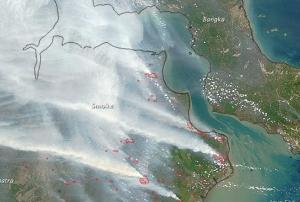
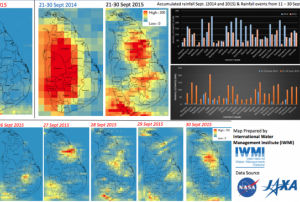
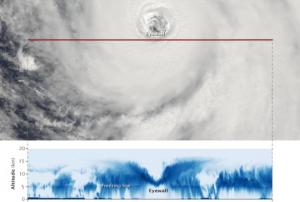
In September 2018, the Indonesian island of Sulawesi was hit by a 7.5 magnitude earthquake. The impact, combined with the tsunami, landslides, and soil liquefaction that followed, “... claimed well over 2000 lives, destroyed homes, buildings, infrastructure and farmland in several districts,” according to the European Space Agency (ESA).
Ten months later, response efforts are now moving into the recovery and rebuilding phase, with satellite information offering important insights to local officials. For example, through a collaboration with the Asian Development Bank, ESA is providing Indonesian officials with hazard-mapping tools derived from Earth observation data, and training in how to most effectively use these resources. “The main purpose of sharing these information products is to help the…
more