Tsunami
Definition
Facts and figures
Further information
UN-SPIDER Regional Support Offices with hazard-specific expertise
Related content on the Knowledge Portal
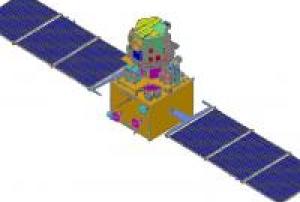
VRSS-1 is Venezuela's first remote sensing satellite.
read more
On May 26, 2011, a contract for the manufacture and launch of the VRSS-1 spacecraft was signed in Caracas, Venezuela, between the government of Venezuela (the Ministry of People’s Power for Science, Technology and Intermediate Industries) and CGWIC (China Great Wall Industry Corporation), a subsidiary of CASC (China Aerospace Science & Technology Corporation).
After launch, the VRSS-1 satellite was renamed in honor of Sebastián Francisco de Miranda (1750-1816), a Venezuelan revolutionary hero, known as ‘Generalissimo’ Francisco de Miranda, who had planned the independence of the Spanish colonies in South America.
Partner organizations in the VRSS-1 program: ABAE is the Space Agency of Venezuela, subordinated and funded by the Venezuelan Ministry of People’s Power for Science, Technology and Innovation (MPPCTI). ABAE is in charge of in-orbit operations, management and application of…20/09/2012SPOT-6 (Système Pour l’Observation de la Terre) is an optical satellite built by Astrium and was successfully launched on September 9, 2012 with SPOT 7 launched on June 30, 2014.
read more
The new generation SPOT-6 and 7 optical satellites feature technological improvements and advanced system performance allowing continuity in the SPOT constellation through to 2024. It is capable of imaging the Earth with a resolution of 1.5 meter panchromatic and 6 meter multispectral (blue, green, red, near-IR) and will offer imaging products to customers in defense, agriculture, deforestation, environmental monitoring, coastal surveillance, engineering, oil, gas and mining industries.
The ability to respond accordingly to changing weather conditions, a reduced timeline for urgent tasking requests and an acquisition capacity of 3 million sq km per satellite shows an increased data capacity and simplified data access, major improvements in this generation of SPOT satellites.
SPOT-6 and…09/09/2012Kanopus-V (also spelling of Canopus-V N1) is an Earth observation minisatellite mission of the Russian Space Agency, Roskosmos and ROSHYDROMET/Planeta. The overall objective is to monitor Earth's surface, the atmosphere, ionosphere, and magnetosphere to detect and study the probability of strong earthquake occurrence.
Essentially, it would be an imaging satellite designed to photograph the Earth surface with a resolution of 2.1 meters and a swath of 20 kilometers with its panchromatic camera and a resolution of 10.5 meters and a swath of 41 kilometers with a multispectral camera. Resulting images could be used for cartography, agricultural planning and similar applications.The Kanopus-V-N1 spacecraft was launched on July 22, 2012 on a Soyuz FG/Fregat vehicle from the Baikonur Cosmodrome, Kazakhstan. The launch provider was Starsem.
Instruments:
read more
PSS (Panchromatic Imaging System)
MSS (Multispectral Imaging System)
MSU-200 (…22/07/2012Today, weather satellites scan the whole Earth, meaning not a single tropical storm or severe weather system goes undetected. The early detection and warnings they provide have saved thousands of lives.
Meteosat data is of unique value to nowcasting of high impact weather in support of safety of life and property.
It has been shown to improve weather forecasts and severe weather warnings which, in turn helps limit damage to property and benefits industry e.g. transport, agriculture and energy.
Meteosat-10 provides the Rapid Scanning Service, delivering more frequent images every five minutes over parts of Europe, Africa and adjacent seas. It also provides Search and Rescue monitoring.Instruments:
read more
GERB (Geostationary Earth Radiation Budget)
MSG Comms (Communications Package for MSG)
SEVIRI (Spinning Enhanced Visible and Infra-Red Imager)
05/07/2012KOMPSAT-3 is an optical high-resolution Korean observation mission of KARI (Korea Aerospace Research Institute). The mission is funded by MEST (Ministry of Education, Science and Technology). The project was started in 2004. The objective is to provide observation continuity from the KOMPSAT-1 and KOMPSAT-2 missions to meet the nation's needs for high-resolution optical imagery required for GIS (Geographical Information Systems) and other environmental, agricultural and oceanographic monitoring applications.
A further goal is to meet the nation's satellite demand and form a technology infrastructure that will make inroads into the world space industry at a stage when the industry is improving the capability to design and develop highly advanced remote sensing satellites.
Instrument: AEISS (Advanced Electronic Image Scanning System)
read more
- 5 spectral…18/05/2012Launched in December 2011, Pleiades is a constellation of two very-high-resolution satellites capable of acquiring imagery of any point on the globe in under 24 hours for civil and military users.
read more
Pleiades has been observing and mapping Earth’s surface at a resolution of just 70 cm every day since December 2011. Comprising the Pleiades 1A and Pleiades 1B satellites, this space imaging system complements the capabilities of the SPOT satellites, which have a wider field of view than Pleiades but lower spatial resolution. What’s more, as Pleiades 1A and 1B are in the same orbit, together they can image anywhere on Earth in less than 24 hours. Pleiades imagery is used for both civil and military applications, for example to track urban expansion, monitor the planet’s active volcanoes or assist road and railway routing, and to locate adversaries’ military installations for mission planning. Pleiades’ key asset is an extremely sensitive optical…17/12/2011ResourceSat-2 is a data continuity mission of ISRO (Indian Space Research Organization) with improved spectral bands of the IRS-P6/ResourceSat-1. Each ResourceSat satellite carries three electrooptical cameras as its payload: LISS-3, LISS-4 and AWiFS. All the three imagers are multispectral pushbroom scanners with linear array CCDs as detectors.
ResourceSat-2 provides continuity and increases the observation timeliness (repetivity) in tandem with ResourceSat-1.
Additionally, the satellite carries an AIS payload for exactEarth (COMDEV), which is known as exactView 2 (EV 2).
Resourcesat-2 was launched in April 2011.Instruments:
read more
AWiFS (Advanced Wide-Field Sensor)
LISS-III (Linear Imaging Self-Scanning Sensor)
S-AIS (Satellite-based Self-Scanning Sensor)
LISS-IV Camera20/04/2011Cartosat-2 is an advanced remote sensing satellite with a single panchromatic camera (PAN) capable of providing scene-specific spot imageries for cartographic applications. The camera is designed to provide imageries with better than one meter spatial resolution and a swath of 10 km. The satellite will have high agility with capability to steer along and across the track up to + 45 degrees. It will be placed in a sun-synchronous polar orbit at an altitude of 630 km. It will have a revisit period of four days. The re-visit can be improved to one day with suitable orbit manoeuvres.
Several new technologies like two mirror on axis single camera, Carbon Fabric Reinforced Plastic based electro optic structure, lightweight, large size mirrors, JPEG like data compression, advanced solid state recorder, high-torque reaction wheels and high performance star sensors are being employed in Cartosat-2.
Instrument: PAN (…
read more12/07/2010The TanDEM-X mission will survey all 150 million square kilometres of Earth's land surface several times over during its three-year mission. Apart from its high measuring-point density (a 12-metre grid) and high vertical accuracy (better than two metres), the elevation model generated by TanDEM-X will have another unrivalled advantage – being entirely homogenous, it will serve as a basis for maps that are globally consistent. Conventional maps are often fragmented along national borders, or difficult to reconcile as they are based on different survey methods or because of time lags between survey campaigns. Together TanDEM-X and TerraSAR-X are form the first configurable synthetic aperture radar interferometer in space. Besides this primary goal, the mission has several secondary objectives based on new and innovative methods such as along-track interferometry, polarimetric synthetic aperture radar interferometry, digital beamforming and bistatic radar. The TanDEM-X…
read more21/06/2010WorldView-2 (WV2) is a commercial imaging satellite of DigitalGlobe Inc. of Longmont, CO, USA (follow-on spacecraft to WorldView-1). The overall objective is to meet the growing commercial demand for high-resolution satellite imagery (0.46 cm Pan, 1.8 m MS at nadir - representing one of the highest available spaceborne resolutions on the market).
In the fall of 2003, DigitalGlobe had received a contract from NGA (National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency) of Washington DC to provide high-resolution imagery from the next-generation commercial imaging satellites. The contract award was made within NGA's NextView program. The NGA requirements called for imagery with a spatial resolution of 0.5 m panchromatic and 2 m MS (Multispectral) data.
The WorldView-2 sensor provides a high resolution panchromatic band and eight (8) multispectral bands; four (4) standard colors (red, green, blue, and near-infrared 1) and four (4) new bands (coastal,…
read more08/10/2009