In the central Andes mountains, satellites have detected ground deformation under way above a major subterranean magma body. The Altiplano–Puna volcanic province is part of an active volcanic arc in South America’s central Andes. Extending through Peru, southwestern Bolivia, Chile and northwestern Argentina, it is home to a number of large calderas formed following catastrophic eruptions. Beneath the surface of Altiplano–Puna, about 17–19 km deep, lies the largest known active magma body in Earth’s continental crust.
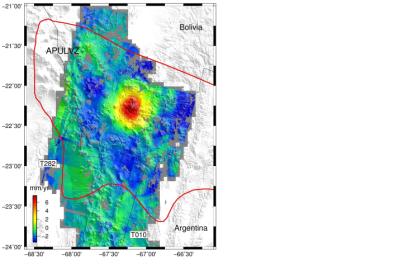
In a study published on 12 October 2012 in Science, scientists used radar data from the ERS and Envisat missions to study an unusual uplift near the Uturuncu volcano, which had been dormant for 270 000 years. The satellites show that the ground in this area has been rising by about 10 mm per year over the past 20 years. The surrounding area, however, is sinking at a slower rate of about 2 mm per year. With the wide-brimmed hat-like shape this creates, the study team has nicknamed this the ‘sombrero uplift’.
In order to get a three-dimensional look at the area of interest, in 2006 the study team had asked ESA to task the ERS-2 and Envisat satellites to acquire more data from both the northbound and southbound orbits over Altiplano-Puna. “It was really important to have good data from different lines of sight, as this allowed us to estimate contributions from vertical and horizontal motion of Earth’s surface, and place crucial constraints on depth and mechanism of the inflation source,” said Yuri Fialko, Professor of Geophysics at the University of California San Diego and the lead author of the paper.