Flood
Definition
Facts and figures
Further information
UN-SPIDER Regional Support Offices with hazard-specific expertise
Related content on the Knowledge Portal
The satellites SPOT 1, 2 and 3 (Satellite Probatoire de l'Observation de la Terre) were the first generation of SPOT earth observation satellites operated by Spot Image.
The first generation SPOT satellites were built on the SPOT Mk.1 bus with a lifetime of three years.
The SPOT satellites were identical, with each carrying two identical HRV (High Resolution Visible) imaging instruments that were able to operate in two modes, either simultaneously or individually. The two spectral modes are panchromatic and multispectral. The panchromatic band had a resolution of 10 meters, and the three multispectral bands (G,R,NIR) have resolutions of 20 meters.
SPOT 3 was orbited on 26 September 1993 on an Ariane-40 H10 rocket. It ended operations in November 1996 due to problems with its stabilization system.
Instruments: 2 HRVs
read more
- 4 spectral bands (1 panchromatic, 3 multispectral)
- imaging swath: 60km x 60km to 80km26/09/1993The satellites SPOT 1, 2 and 3 (Satellite Probatoire de l'Observation de la Terre) were the first generation of SPOT earth observation satellites operated by Spot Image.
The first generation SPOT satellites were built on the SPOT Mk.1 bus with a lifetime of three years.
The SPOT satellites were identical, with each carrying two identical HRV (High Resolution Visible) imaging instruments that were able to operate in two modes, either simultaneously or individually. The two spectral modes are panchromatic and multispectral. The panchromatic band had a resolution of 10 meters, and the three multispectral bands (G,R,NIR) have resolutions of 20 meters.
SPOT-2 was launched on 22 January 1990, on an Ariane-40 H10 rocket. It operated until July 2009. Its orbit was lowered to ensure reentry within 25 years.
Instruments: 2 HRVs
read more
- 4 spectral bands (1 panchromatic, 3 multispectral)
- imaging swath: 60km x 60km to 80km22/01/1990The satellites SPOT 1, 2 and 3 (Satellite Probatoire de l'Observation de la Terre) were the first generation of SPOT earth observation satellites operated by Spot Image.
The first generation SPOT satellites were built on the SPOT Mk.1 bus with a lifetime of three years.
The SPOT satellites were identical, with each carrying two identical HRV (High Resolution Visible) imaging instruments that were able to operate in two modes, either simultaneously or individually. The two spectral modes are panchromatic and multispectral. The panchromatic band had a resolution of 10 meters, and the three multispectral bands (G,R,NIR) have resolutions of 20 meters.
SPOT 1 was launched with the last Ariane-1 rocket on 22 February 1986. At the end of operations in 2003, the orbit was lowered to gradually lose altitude until reentry.
Instruments: 2 HRVs
read more
- 4 spectral bands (1 panchromatic, 3 multispectral)
- imaging swath: 60km x 60km to 80km22/02/1986Landsat 5 was launched from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on March 1, 1984, and like Landsat 4, carried the Multispectral Scanner (MSS) and the Thematic Mapper (TM) instruments. Landsat 5 delivered Earth imaging data nearly 29 years - and set a Guinness World Record For 'Longest Operating Earth Observation Satellite', before being decommissioned on June 5, 2013.
read more
The Landsat 5 satellite orbited the the Earth in a sun-synchronous, near-polar orbit, at an altitude of 705 km (438 mi), inclined at 98.2 degrees, and circled the Earth every 99 minutes. The satellite had a 16-day repeat cycle with an equatorial crossing time: 9:45 a.m. +/- 15 minutes. Landsat 5 data were acquired on the Worldwide Reference System-2 (WRS-2) path/row system, with swath overlap (or sidelap) varying from 7 percent at the Equator to a maximum of approximately 85 percent at extreme latitudes.
Landsat 5 long outlived its…01/03/1984Landsat 4 was launched on July 16, 1982. The Landsat 4 spacecraft was significantly different than that of the previous Landsats, and Landsat 4 did not carry the RBV instrument.
read more
In addition to the Multispectral Scanner System (MSS) instrument, Landsat 4 (and Landsat 5) carried a sensor with improved spectral and spatial resolution, i.e., the new satellites could see a wider (and more scientifically-tailored) portion of the electromagnetic spectrum and could see the ground in greater detail. This new instrument was known as the Thematic Mapper (TM).
Landsat 4 was kept in orbit for housekeeping telemetry command and tracking data (which it downlinked via a separate data path, the S-band) until it was decommissioned in 2001.
While Landsat 4 was built and launched by NASA, NOAA initially oversaw the operations of the satellite. Landsat 4 operations were contracted out to the Earth Observation Satellite Company (…16/07/1982Landsat 3 was launched on March 5, 1978, three years after Landsat 2.
read more
The Landsat program’s technical and scientific success together with political and economic pressures lead to the decision to commercialize an operational Landsat. To this end, responsibility was slated to shift from NASA (a research and development agency) to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), the agency charged with operating the weather satellites. This was done via Presidential Directive/NSC-54 signed on Nov. 16, 1979 which assigned NOAA “management responsibility for civil operational land remote sensing activites.” (However, operational management was not transfered from NASA to NOAA until 1983).
Landsat 3 carried the same sensors as its predecessor: the Return Beam Vidicon (RBV) and the Multispectral Scanner (MSS). The RBV instrument on-board Landsat 3 had…05/03/1978Landsat 2 was launched into space onboard a Delta 2910 rocket from Vandenberg Air Force Base, California on January 22, 1975, two and a half years after Landsat 1. Originally named ERTS-B (Earth Resource Technology Satellite B), the spacecraft was renamed Landsat 2 prior to launch. The second Landsat was still considered an experimental project and was operated by NASA.
Landsat 2 carried the same sensors as its predecessor: the Return Beam Vidicon (RBV) and the Multispectral Scanner System (MSS).
On February 25, 1982 after seven years of service, Landsat 2 was removed from operations due to yaw control problems; it was offically decommissioned on July 27, 1983.Instruments:
read more
Return Beam Vidicon (RBV)
Multispectral Scanner (MSS)
22/01/1975Landsat 1 was launched on July 23, 1972; at that time the satellite was known as the Earth Resources Technology Satellite (ERTS). It was the first Earth-observing satellite to be launched with the express intent to study and monitor our planet’s landmasses. To perform the monitoring, Landsat 1 carried two instruments: a camera system built by the Radio Corporation of America (RCA) called the Return Beam Vidicon (RBV), and the Multispectral Scanner (MSS) built by the Hughes Aircraft Company. The RBV was supposed to be the prime instrument, but the MSS data were found to be superior. In addition, the RBV instrument was the source of an electrical transient that caused the satellite to briefly lose altitude control, according to the Landsat 1 Program Manager, Stan Weiland.
read more
To help understand the data and to explore the potential applications of this new technology, NASA oversaw 300 private research investigators. Nearly one third of these were international scientists…23/07/1972Recommended Practice: Flood Mapping Practice Using Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 Imagery
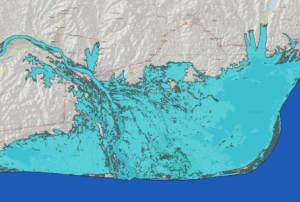
UN-SPIDER has published a new Recommended Practice that leverages both Sentinel-1 Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) and Sentinel-2 optical imagery to improve flood detection and mapping. Developed by the Regional Centre for Mapping of Resources for Development (RCMRD), this method offers a multispectral and radar-based approach to identifying flood-affected areas with greater precision, especially in regions with persistent cloud cover or challenging terrain.
The practice outlines a clear workflow using Google Earth Engine and QGIS to generate flood extent maps that can support emergency response and early recovery efforts. The integration of radar and optical data helps overcome the limitations of relying on a single satellite source, enabling consistent monitoring even during adverse weather conditions.
This methodology was applied to flood events in Mozambique, demonstrating how…
read more18/06/2025- Storm surges and tidal waves are global phenomena that considerably affect human populations in coastal and island regions. According to the Guide to Storm Surge Forecasting published by the World Meteorological Organization in 2011, storm surges can be defined as ‘oscillations of the water level in a coastal or inland body of water in the time range of a few minutes to a few days, resulting from forcing from atmospheric weather systems. According to this definition, the so-called wind waves, which have durations on the order of several seconds, are excluded’. Storm surges are a coastal…Regional Support Offices mentioned: