Pollution
UN-SPIDER Regional Support Offices with hazard-specific expertise
Related content on the Knowledge Portal
Intensive capacity development sessions for Pacific island countries (Cook Islands, Fiji, Kiribati, Micronesia (the Federated States of), Samoa, Solomon Islands, Tonga, and Vanuatu).
The project aims to enhance institutional and technical capacity for using geospatial data and technology applications and promote regional cooperation for sharing geospatial data for disaster management in Pacific island countries.
Publishing institution:Developed for the needs of the ASEAN sub-region in Asia and the Pacific, the handbooks can also be adapted for use in other regions.
The handbooks have been developed through expert working groups, in collaboration with United Nations partners including UNOOSA/UN-SPIDER, UNITAR-UNOSAT, and OCHA. As well as extensive consultation with space agencies, national disaster management authorities and regional institutions, including GISTDA, LAPAN, ASEAN Coordinating Centre for Humanitarian Assistance on Disaster Management and Asian Institute of Technology.
Publishing institution:For a comprehensive and objective analysis of the settlement patterns, the DLR additionally developed an approach to display the spatial networks between the mapped settlements. It enables the computation of various form and centrality measures to characterize settlement patterns, at different spatial units, ranging from global to local scale.
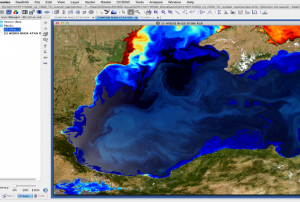
Publishing institution:CEMS is a core service of the European Union’s Earth Observation programme Copernicus. It supports all phases of the disaster management cycle by delivering warnings and risk assessments of floods and forest fires and by providing geospatial information derived from satellite images on the impact of natural and man-made disasters all over the world (before, during or after a crisis). The two Mapping services of CEMS (Rapid Mapping, Risk and Recovery Mapping) are delivering products since April 2012. The Risk & Recovery Mapping provided for example information for preparedness, disaster risk assessment and risk reduction related to earthquakes in Nepal, several post-disaster assessments for flood and fire events, reconstruction and recovery monitoring in Haiti, and multi-risk assessments for the Azores Islands in Portugal.
CEMS is coordinated by the European Commission (joint coordination between the Directorate Generals ECHO, JRC, GROW). Activation requests…
read morePublishing institution:- The main objective of the SENTINEL-3 mission is to monitor sea and land surface
temperature, sea surface topography and ocean and land surface colour with high accuracy and reliability. The high resolution data is meant to support ocean forecasting systems, environmental monitoring and climate monitoring.
ESA and EUMETSAT will jointly operate the SENTINEL-3 mission and bothy institutions provide access to the processed data.
Sentinel 3 carries four main instruments: the OLCI, SLSTR, Altimetry and a MWR Microwave Radiometer.
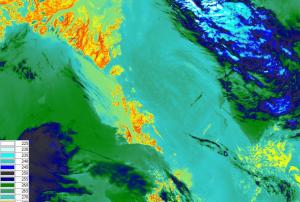
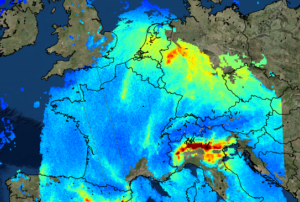
Publishing institution: On 11 July 2018, the first data on air quality by Copernicus Sentinel-5P was released. Presenting a great improvement in accuracy for monitoring air pollutants, these maps show the presence of trace gases such as ozone, nitrogen dioxide and carbon monoxide. Additional data products such as the Aerosol index can provide information on atmospheric volcanic ash for aviation safety and on high levels of UV radiation.
Sentinel-5 Precursor was created to reduce the data gap between Envisat and Sentinel-5, which is set to be launched ~2021. Sentinel-5P is part of the constellation of SENTINEL-4, -5 and -5 precursor (S4, S5, S5P), developed by the European Space Agency, to gather information on atmospheric variables to support European policies.
High expectations are set on Sentinel 5P, as it carries the Tropomi instrument - the most advanced…
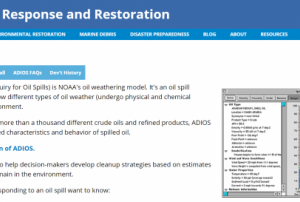
read more13/07/2018- ADIOS® (Automated Data Inquiry for Oil Spills) is NOAA's oil weathering model. It's an oil spill response tool that models how different types of oil weather (undergo physical and chemical changes) in the marine environment.
Working from a database of more than a thousand different crude oils and refined products, ADIOS quickly estimates the expected characteristics and behaviour of spilled oil.Publishing institution: - The NOAA Unit Converter for Oil Spills (NUCOS) is a simple desktop tool that converts basic units of velocity, mass, length, etc., but more specifically, converts units that are unique to oil spill response. NUCOS includes some of the lesser known units used in managing oil and chemical spills. For example, it converts the units for oil volume, viscosity, and density from the conversion list of the Dispersant Mission Planner 2, a tool that helps spill responders assess dispersant application system performance.Publishing institution: