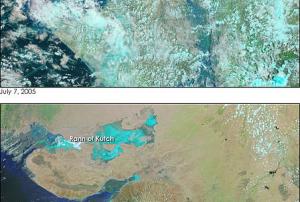
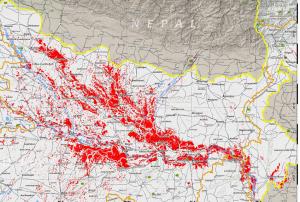
On July 25, 2013 the Indian meteorological satellite INSAT-3D was successfully launched, equipped with search and rescue payload that will facilitate speedy search and rescue operations to India and surrounding regions. These mechanisms on board of the INSAT-3D pick up and relay alert signals originating from the distress beacons of maritime, aviation and land based users and relays them to the mission control centre, improving the emergency response.
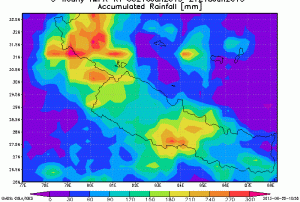
Moreover, the satellite carries an atmospheric sounding system that is expected to add a new dimension to weather monitoring with a 6-channel imager and a 19-channel infrared sounder that will provide full disc imagery every 30 minutes over the Indian Ocean and surrounding regions.
INSAT-3D stands for Indian National Satellite - 3D and is part of the INSAT-3 series developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). The satellite was launched by an Ariane-5 launch vehicle from the spaceport of Kourou in French...
more