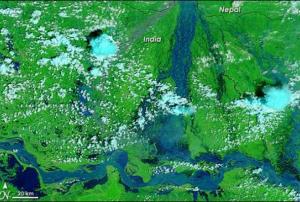
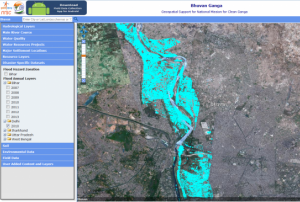
The Government of India has established 176 flood forecasting stations across the country which would help to monitor river flooding during monsoons. The stations use information captured by Indian satellites, including near-real time flood inundation maps provided by the National Remote Sensing Centre.
The Central Water Commission (CWC), belonging to the Ministry Water Resources, is in charge of predicting floods in major rivers and their tributaries through rainfall-runoff models provided by the India Meteorological Department. CWC has also used remote sensing imagery and geographical data for monitoring water bodies in the Himalayan region.
Uma Bharti, Minister of Water Resources, stated that "it (Ministry) has set up 176 flood forecasting stations in the country where flood forecasts are issued in every monsoon whenever water level or the inflow in a river exceeds the predefined criteria."
more