
Space technologies and geospatial data can support governments in improving situational awareness and responding to the COVID-19 outbreak. Several institutions have published information products, such as web maps of confirmed infections and deaths, that are making use of the advantages of GIS. Others have used space technologies to track pollution levels across the world, highlighting a drop due to the restrictions imposed as a result of the pandemic. Yet others are using a combination of global navigation satellite systems technologies to map the position of critical infrastructure in geographical areas where there are reported cases.
The United Nations Office for Outer Space Affairs, through its UN-SPIDER programme, has created this COVID-19 emergency response overview page to facilitate the discovery of examples of contributions of space technologies to addressing COVID-19 that are being published by government agencies, international and regional organizations, academia, civil society and the private sector. To find out more about the efforts of UNOOSA in advancing the use of space-based solutions for global health, please visit this web page.
To support users in finding relevant content, the list below can be filtered by keywords as well as format of the resource. The list does not seek to be exhaustive, nor to recommend particular sources, but to provide a selection of examples of how space technologies and the space community support response efforts to COVID-19.
UNOOSA will host a webinar on Space4Health on 14 May at 10am and 4pm Vienna, Austria time (UTC+2).
If you are using space technologies for responding to the COVID-19 pandemic and would like your work to be included on this page, please use this form to submit details.
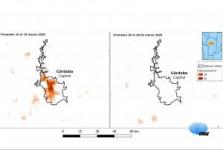
Maps produced by the National Space Activities Commission (CONAE) of Argentina based on satellite images show the notable decrease in nitrogen dioxide (NO₂) during the first days following compulsory isolation due to the COVID-19 outbreak compared to the previous days. The satellite measurements complement those of the surface monitoring... Read more
Tag: (Indirect) impact of the virus
The Copernicus satellites have been observing rapid changes in the environment in regions that have gone into lockdown amid COVID-19 crisis. By measuring concentration of NO2 from space, ESA has been able to indirectly determine the impact of COVID-19 measures on industrial and economy activities, as well drops in air pollution which in turn... Read more
Tag: (Indirect) impact of the virus

A free app that helps people observe social distancing to slow the spread of coronavirus is about to launch.
Devised by Lanterne, a UK start-up company supported by ESA, it uses satellite data and artificial intelligence technologies to identify where people are congregating anywhere in the world.
Tag: Situational data

Copernicus Hackathon Sofia is a competition for the development of new applications based on Copernicus Earth observation data and services, under the European Copernicus program. In April 2019, the first edition of Copernicus Hackathon Sofia was successfully held, which aroused... Read more
Tag: Emergency mapping, (Indirect) impact of the virus

This two-part study published by SpaceWatch.Global examines the role of satellite technologies in detecting and monitoring the ongoing outbreak of the Coronavirus in China. It provides examples for the use of all types of space technologies in response to COVID-19 in the country.
... Read more
Tag: (Indirect) impact of the virus, Tele-health

To see how Earth-observing missions could be further used to explore the effects of COVID-19, ESA has issued a new call for proposals. The aim is to understand how satellite data can be used, for example, to map changes around transport networks, commercial ports and heavy industry such as oil refineries. This new call has been added to the... Read more
Tag: Research opportunities
The satellite industry has been ensuring broad connectivity and service continuity for public and private users during the COVID-19 pandemic. Satellite application is being used to enable communications between workers, between families and friends, and between teachers and students via various distance communication and learning tools. Space... Read more
Tag: Risk assessments, Tele-health
The International Journal of Remote Sensing is inviting new contributions on how the use of remote sensing can help with COVID-19 and its impacts. Such areas may include agriculture and farming, civil contingency planning and management, climate change, countryside, education - higher and further, education – schools, emergency planning,... Read more
Tag: (Indirect) impact of the virus, Research opportunities

The COVID-19 emergency is pressuring the healthcare sector and the practice of medicine all around the world. In this tough period, it is important to cast light on the unprecedented challenges posed in the hospitals to avoid putting at risk those swathes of the population (elderlies, immunocompromised, multi-pathological patients, etc.), that... Read more
Tag: Tele-health

In a joint initiative with the European Space Agency (ESA), the UK Space Agency (UKSA) has called on industry and universities help develop technology and equipment – from hand sanitiser to ventilators – to support the National Health Service (NHS). Space-enabled solutions could include satellite communications, satellite navigation... Read more
Tag: Situational data, Risk assessments, Emergency mapping

In support to the UN Secretary-General’s initiative in assisting Member States at the COVID-19 crisis, the UN Department for Economic and Social Affairs requests inputs in response to its Call for Technology Solutions for addressing the COVID-19 pandemic and its immediate impacts. This effort is undertaken in the context of the UN... Read more
Tag: Research opportunities, UN activities
UP42 is offering free access to its platform for non-profits, universities, and governments working on an initiative related to COVID-19. UP42 will allow free access to over 20 data sources and 50 processing algorithms, including satellite imagery, weather data, and machine learning-based object detection and classification, as well as the... Read more
Tag: Situational data, Risk assessments, (Indirect) impact of the virus, Research opportunities

