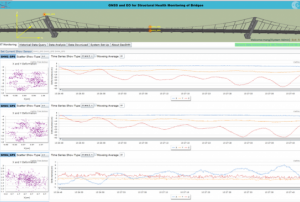
The Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) launched two Earth observation satellites on 16 September from Sriharikota where the Satish Dhawan Space Center is located. NovaSAR S1-4, which were developed in and will be operated from the United Kingdom, will provide Earth observation data, including for disaster and risk management.
The satellites were constructed by Surrey Satellite Technology Limited, a UK-based company that, in partnership with ISRO (the vehicle was developed by Vikram Sarabhai Space Center), has made possible the commercial PSLV-C42 mission to launch the satellite. This is not the only foreign satellite launched by ISRO. Since 1999, the space organization has released several devices from international…
more