Inundación
Definition
Facts and figures
Further information
UN-SPIDER Regional Support Offices with hazard-specific expertise
Related content on the Knowledge Portal
For a comprehensive and objective analysis of the settlement patterns, the DLR additionally developed an approach to display the spatial networks between the mapped settlements. It enables the computation of various form and centrality measures to characterize settlement patterns, at different spatial units, ranging from global to local scale.
read morePublishing institution:CEMS is a core service of the European Union’s Earth Observation programme Copernicus. It supports all phases of the disaster management cycle by delivering warnings and risk assessments of floods and forest fires and by providing geospatial information derived from satellite images on the impact of natural and man-made disasters all over the world (before, during or after a crisis). The two Mapping services of CEMS (Rapid Mapping, Risk and Recovery Mapping) are delivering products since April 2012. The Risk & Recovery Mapping provided for example information for preparedness, disaster risk assessment and risk reduction related to earthquakes in Nepal, several post-disaster assessments for flood and fire events, reconstruction and recovery monitoring in Haiti, and multi-risk assessments for the Azores Islands in Portugal.
CEMS is coordinated by the European Commission (joint coordination between the Directorate Generals ECHO, JRC, GROW). Activation requests...
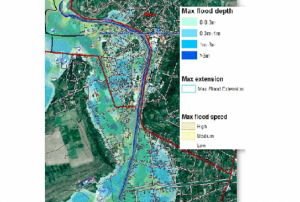
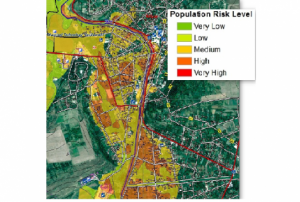
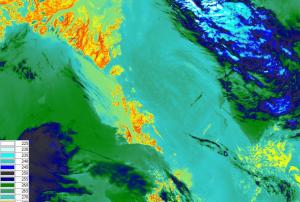
read morePublishing institution:- As a means of emergency response after a flooding event or inland inundation, flood mapping helps to estimate the extent of the flood on a large scale. It is a basis of coordinating appropriate recovery activities, rehabilitation and prevention measures for possible upcoming events. This UN-SPIDER Recommended Practice on flood mapping and damage assessment explains the use of Sentinel-2 (S2) optical satellite data from the European Space Agency (ESA), which acquires data in 13 spectral bands. It provides hands-on practice to calculate the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) to determine...Regional Support Offices mentioned:
The International Charter “Space and Major Disasters” has been activated for floods in Venezuela on 15 August and in India on 16 August.
Floods in Venezuela
In Venezuela, persistent heavy rain and swollen rivers have caused severe flooding, which has affected over 10,000 people in the Venezuelan provinces of Amazonas, Apure, Bolivar and Anzoategui. The Orinoco river reached its highest levels in 40 years, leading the river to burst its banks in my places. Local authorities have set up an aerial bridge over the river so supplies of food, medicine and aid can reach the affected populations. Major arterial roads have also been closed, isolating some areas and further hampering emergency response efforts.
The red alert for rain and flooding is set to be in place until the end of August, with further rain forecast in the coming weeks.
The Charter activation was made by Venezuelan civil protection...
read more16/08/2018The United Nations Office for Outer Space Affairs (UNOOSA) and the United Nations Institute for Training and Research (UNITAR) Operational Satellite Applications Programme (UNOSAT) have jointly activated the International Charter “Space and Major Disasters” for the recent floods in Lao People’s Democratic Republic on 24 July 2018. UNOOSA activated the Charter on behalf of the country’s Ministry of Science and Technology and Department of Disaster Management and Climate, while UNITAR-UNOSAT activated the emergency mechanism on behalf of the World Food Program (WFP). At least 20 people have been killed and hundreds of people remain missing after floods struck the country's Attapeu province. The collapse of the Xe-Pian Xe-Namnoy hydroelectric dam released 5 billion cubic meters of water downstream, flooding at least 7 villages and washing away homes. Emergency responders are now working to rescue people from the area, evacuate them to emergency shelters and search for the missing....
read moreRegional Support Offices mentioned:27/07/2018At least 20 people have been killed and hundreds of people remain missing after floods struck the Attapeu province of Lao People's Democratic Republic. The collapse of the Xe-Pian Xe-Namnoy hydroelectric dam released 5 billion cubic meters of water downstream, flooding at least 7 villages and washing away homes.
Emergency responders are working to rescue people from the area, evacuate them to emergency shelters and search for the missing. Local authorities have also appealed to government bodies and other communities to provide emergency aid such as clothing, food, drinking water and medicine.
The International Charter was jointly activated by the United Nations Office for Outer Space Affairs (UNOOSA) and the United Nations Institute for Training and Research (UNITAR) Operational Satellite Applications Programme (UNOSAT) for major floods in Lao People's Democratic Republic on 24 July 2018. UNOOSA activated the Charter on behalf of the country's...read more- The main objective of the SENTINEL-3 mission is to monitor sea and land surface
temperature, sea surface topography and ocean and land surface colour with high accuracy and reliability. The high resolution data is meant to support ocean forecasting systems, environmental monitoring and climate monitoring.
ESA and EUMETSAT will jointly operate the SENTINEL-3 mission and bothy institutions provide access to the processed data.
Sentinel 3 carries four main instruments: the OLCI, SLSTR, Altimetry and a MWR Microwave Radiometer.
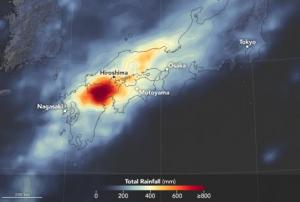
Publishing institution: The International Charter “Space and Major Disasters” was activated on 7 July for a major flooding disaster which has hit Japan, the worst the country has experienced in 36 years.
Heavy rains, which first started at the end of June 2018, caused flash flooding and deadly landslides across western and central Japan from 5 July. Over 200 fatalities have been recorded in the country so far as a result of the disaster. The rains which caused the flooding appear to have been caused by warm, humid air flowing from the Pacific Ocean and by remnants of Typhoon Prapiroon, both of which intensified the seasonal rain front. Some 8.63 million people across 23 prefectures in Japan have been...
read more16/07/2018India’s Central Water Commission (CWC) has signed a Collaboration Agreement with Google that will help crisis management agencies deal with extreme hydrological events, such as floods, more effectively.
The agreement allows CWC to make use of Google’s artificial intelligence, machine learning and geospatial mapping expertise for effective water management and flood forecasting. The agreement will also help CWC to better disseminate flood related information through different platforms developed by Google.
Under this Agreement, CWC and Google will share technical expertise in different fields related to flood management, including geospatial flood mapping and analysis of hydrological observation data. The agreement also facilitates collaboration on improving flood prediction systems, which will help provide location-targeted, actionable flood warnings; a high priority research project utilizing Google Earth Engine to help...
read more10/07/2018