United
Nations
Office for Outer Space Affairs
UN-SPIDER Knowledge Portal
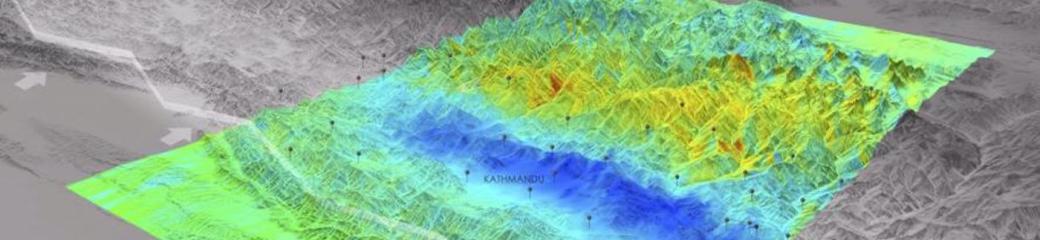
Sudden movement of a block of the Earth’s crust along a geological fault and associated ground shaking (IRDR Glossary).
Earthquake can be defined as the shaking of earth caused by waves moving on and below the earth's surface and causing: surface faulting, tremors vibration, liquefaction, landslides, aftershocks and/or tsunamis (WHO).
The size or magnitude of earthquakes is determined by measuring the amplitude of the seismic waves recorded on a seismograph and the distance of the seismograph from the earthquake. These are put into a formula which converts them to a magnitude, which is a measure of the energy released by the earthquake. For every unit increase in magnitude, there is roughly a thirty-fold increase in the energy released. Earthquake magnitude was traditionally measured on the Richter scale. It is often now calculated from seismic moment, which is proportional to the fault area multiplied by the average displacement on the fault (Australian Government).
There are four different types of earthquakes: tectonic, volcanic, collapse and explosion.