Kenya’s president has declared the worsening drought in the country a national disaster.
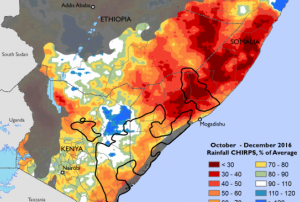
According to the National Drought Management Authority (NDMA) the drought has been worsening in most Kenyan counties, now affecting nearly half the country. Forage conditions are drier than usual because of lower than usual rainfall conditions and also the extended dry period between the short and long rains in 2016. The number of people in need of food has risen from 1.3 million to 2.7 million last year.
Low levels of rainfall affected the crop performance in certain parts of the country, especially around Lake Victoria and in parts of the western and central region. Maize, beans and sorghum yields have experienced a significant drop of nearly 50% and in some counties, maize is said to be near total failure.
The drought has also left the livestock in danger, causing unusual patterns of livestock migration. According to FAO’s Joseph Matere, it is going to get…
more